Interactive periodic table with up-to-date element property data collected from authoritative sources. Look up chemical element names, symbols, atomic masses and other properties, visualize trends, or even test your elements knowledge by playing a periodic table game! Atomic radius of all the elements are mentioned in the chart below.(Note: Below mentioned radii are the van der Waals radius in picometer (pm)).
The elements of the periodic table sorted by atomic mass
click on any element's name for further information on chemical properties, environmental data or health effects.
This list contains the 118 elements of chemistry.
| The chemical elements of the periodic chart sorted by: | Atomic Mass | Name chemical element | Symbol | Atomic number |
| - Name alphabetically | 1.0079 | Hydrogen | H | 1 |
| - Atomic number | 4.0026 | Helium | He | 2 |
| - Symbol | 6.941 | Lithium | Li | 3 |
| - Atomic Mass | 9.0122 | Beryllium | Be | 4 |
| - Electronegativity | 10.811 | Boron | B | 5 |
| - Density | 12.0107 | Carbon | C | 6 |
| - Melting point | 14.0067 | Nitrogen | N | 7 |
| - Boiling point | 15.9994 | Oxygen | O | 8 |
| - Vanderwaals radius | 18.9984 | Fluorine | F | 9 |
| - Year of discovery | 20.1797 | Neon | Ne | 10 |
| - Inventor surname | 22.9897 | Sodium | Na | 11 |
| - Elements in earthcrust | 24.305 | Magnesium | Mg | 12 |
| - Elements in human body | 26.9815 | Aluminum | Al | 13 |
| - Covalenz radius | 28.0855 | Silicon | Si | 14 |
| - Ionization energy | 30.9738 | Phosphorus | P | 15 |
For chemistry students and teachers: The tabular chart on the right is arranged by Atomic mass (weight). The lightest chemical element is Hydrogen and the heaviest is Hassium. The unity for atomic mass is gram per mol. Please note that the elements do not show their natural relation towards each other as in the Periodic system. There you can find the metals, semi-conductor(s), non-metal(s), inert noble gas(ses), Halogens, Lanthanoides, Actinoids (rare earth elements) and transition metals. | 32.065 | Sulfur | S | 16 |
| 35.453 | Chlorine | Cl | 17 | |
| 39.0983 | Potassium | K | 19 | |
| 39.948 | Argon | Ar | 18 | |
| 40.078 | Calcium | Ca | 20 | |
| 44.9559 | Scandium | Sc | 21 | |
| 47.867 | Titanium | Ti | 22 | |
| 50.9415 | Vanadium | V | 23 | |
| 51.9961 | Chromium | Cr | 24 | |
| 54.938 | Manganese | Mn | 25 | |
| 55.845 | Iron | Fe | 26 | |
| 58.6934 | Nickel | Ni | 28 | |
| 58.9332 | Cobalt | Co | 27 | |
| 63.546 | Copper | Cu | 29 | |
| 65.39 | Zinc | Zn | 30 | |
| 69.723 | Gallium | Ga | 31 | |
| 72.64 | Germanium | Ge | 32 | |
| 74.9216 | Arsenic | As | 33 | |
| 78.96 | Selenium | Se | 34 | |
| 79.904 | Bromine | Br | 35 | |
| 83.8 | Krypton | Kr | 36 | |
| 85.4678 | Rubidium | Rb | 37 | |
| 87.62 | Strontium | Sr | 38 | |
| 88.9059 | Yttrium | Y | 39 | |
| 91.224 | Zirconium | Zr | 40 | |
| 92.9064 | Niobium | Nb | 41 | |
| 95.94 | Molybdenum | Mo | 42 | |
| 98 | Technetium | Tc | 43 | |
| 101.07 | Ruthenium | Ru | 44 | |
| 102.9055 | Rhodium | Rh | 45 | |
| 106.42 | Palladium | Pd | 46 | |
| 107.8682 | Silver | Ag | 47 | |
| 112.411 | Cadmium | Cd | 48 | |
| 114.818 | Indium | In | 49 | |
| 118.71 | Tin | Sn | 50 | |
| 121.76 | Antimony | Sb | 51 | |
| 126.9045 | Iodine | I | 53 | |
| 127.6 | Tellurium | Te | 52 | |
| 131.293 | Xenon | Xe | 54 | |
| 132.9055 | Cesium | Cs | 55 | |
| 137.327 | Barium | Ba | 56 | |
| 138.9055 | Lanthanum | La | 57 | |
| 140.116 | Cerium | Ce | 58 | |
| 140.9077 | Praseodymium | Pr | 59 | |
| 144.24 | Neodymium | Nd | 60 | |
| 145 | Promethium | Pm | 61 | |
| 150.36 | Samarium | Sm | 62 | |
| 151.964 | Europium | Eu | 63 | |
| 157.25 | Gadolinium | Gd | 64 | |
| 158.9253 | Terbium | Tb | 65 | |
| 162.5 | Dysprosium | Dy | 66 | |
| 164.9303 | Holmium | Ho | 67 | |
| 167.259 | Erbium | Er | 68 | |
| 168.9342 | Thulium | Tm | 69 | |
| 173.04 | Ytterbium | Yb | 70 | |
| 174.967 | Lutetium | Lu | 71 | |
| 178.49 | Hafnium | Hf | 72 | |
| 180.9479 | Tantalum | Ta | 73 | |
| 183.84 | Tungsten | W | 74 | |
| 186.207 | Rhenium | Re | 75 | |
| 190.23 | Osmium | Os | 76 | |
| 192.217 | Iridium | Ir | 77 | |
| 195.078 | Platinum | Pt | 78 | |
| 196.9665 | Gold | Au | 79 | |
| 200.59 | Mercury | Hg | 80 | |
| 204.3833 | Thallium | Tl | 81 | |
| 207.2 | Lead | Pb | 82 | |
| 208.9804 | Bismuth | Bi | 83 | |
| 209 | Polonium | Po | 84 | |
| 210 | Astatine | At | 85 | |
| 222 | Radon | Rn | 86 | |
| 223 | Francium | Fr | 87 | |
| 226 | Radium | Ra | 88 | |
| 227 | Actinium | Ac | 89 | |
| 231.0359 | Protactinium | Pa | 91 | |
| 232.0381 | Thorium | Th | 90 | |
| 237 | Neptunium | Np | 93 | |
| 238.0289 | Uranium | U | 92 | |
| 243 | Americium | Am | 95 | |
| 244 | Plutonium | Pu | 94 | |
| 247 | Curium | Cm | 96 | |
| 247 | Berkelium | Bk | 97 | |
| 251 | Californium | Cf | 98 | |
| 252 | Einsteinium | Es | 99 | |
| 257 | Fermium | Fm | 100 | |
| 258 | Mendelevium | Md | 101 | |
| 259 | Nobelium | No | 102 | |
| 261 | Rutherfordium | Rf | 104 | |
| 262 | Lawrencium | Lr | 103 | |
| 262 | Dubnium | Db | 105 | |
| 264 | Bohrium | Bh | 107 | |
| 266 | Seaborgium | Sg | 106 | |
| 268 | Meitnerium | Mt | 109 | |
| 272 | Roentgenium | Rg | 111 | |
| 277 | Hassium | Hs | 108 | |
| Darmstadtium | Ds | 110 | ||
| Copernicium | Cn | 112 | ||
| Nihonium | Nh | 113 | ||
| Flerovium | Fl | 114 | ||
| Moscovium | Mc | 115 | ||
| Livermorium | Lv | 116 | ||
| Tennessine | Ts | 117 | ||
| Oganesson | Og | 118 |
Click here: for a schematic overview of the periodic table of elements in chart form
Do you need to know the weight of some molecules? Try our Molecular Weight Calculator!
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com

Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope. (Atomic mass is also referred to as atomic weight, but the term 'mass' is more accurate.)
For instance, it can be determined experimentally that neon consists of three isotopes: neon-20 (with 10 protons and 10 neutrons in its nucleus) with a mass of 19.992 amu and an abundance of 90.48%, neon-21 (with 10 protons and 11 neutrons) with a mass of 20.994 amu and an abundance of 0.27%, and neon-22 (with 10 protons and 12 neutrons) with a mass of 21.991 amu and an abundance of 9.25%. The average atomic mass of neon is thus:
| 0.9048 | × | 19.992 amu | = | 18.09 amu |
| 0.0027 | × | 20.994 amu | = | 0.057 amu |
| 0.0925 | × | 21.991 amu | = | 2.03 amu |
| 20.18 amu |
The atomic mass is useful in chemistry when it is paired with the mole concept: the atomic mass of an element, measured in amu, is the same as the mass in grams of one mole of an element. Thus, since the atomic mass of iron is 55.847 amu, one mole of iron atoms would weigh 55.847 grams. The same concept can be extended to ionic compounds and molecules. One formula unit of sodium chloride (NaCl) would weigh 58.44 amu (22.98977 amu for Na + 35.453 amu for Cl), so a mole of sodium chloride would weigh 58.44 grams. One molecule of water (H2O) would weigh 18.02 amu (2×1.00797 amu for H + 15.9994 amu for O), and a mole of water molecules would weigh 18.02 grams.
Atomic Element Mn
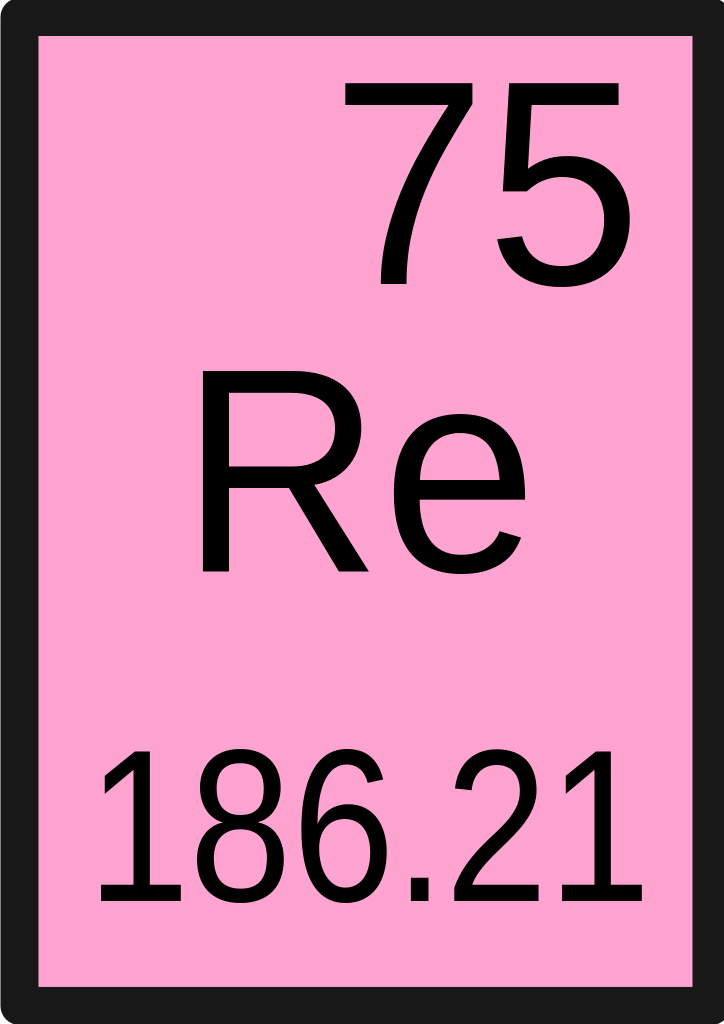
Do you need to know the weight of some molecules? Try our Molecular Weight Calculator!
Lenntech (European Head Office)
Distributieweg 3
2645 EG Delfgauw
The Netherlands
Phone: +31 152 610 900
fax: +31 152 616 289
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech USA LLC (Americas)
5975 Sunset Drive
South Miami, FL 33143
USA
Phone: +1 877 453 8095
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Lenntech DMCC (Middle East)
Level 5 - OFFICE #8-One JLT Tower
Jumeirah Lake Towers
Dubai - U.A.E.
Phone: +971 4 429 5853
e-mail: info@lenntech.com
Copyright © 1998-2021 Lenntech B.V. All rights reserved
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as daltons, D). The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the abundance of that particular isotope. (Atomic mass is also referred to as atomic weight, but the term 'mass' is more accurate.)
For instance, it can be determined experimentally that neon consists of three isotopes: neon-20 (with 10 protons and 10 neutrons in its nucleus) with a mass of 19.992 amu and an abundance of 90.48%, neon-21 (with 10 protons and 11 neutrons) with a mass of 20.994 amu and an abundance of 0.27%, and neon-22 (with 10 protons and 12 neutrons) with a mass of 21.991 amu and an abundance of 9.25%. The average atomic mass of neon is thus:
| 0.9048 | × | 19.992 amu | = | 18.09 amu |
| 0.0027 | × | 20.994 amu | = | 0.057 amu |
| 0.0925 | × | 21.991 amu | = | 2.03 amu |
| 20.18 amu |
The atomic mass is useful in chemistry when it is paired with the mole concept: the atomic mass of an element, measured in amu, is the same as the mass in grams of one mole of an element. Thus, since the atomic mass of iron is 55.847 amu, one mole of iron atoms would weigh 55.847 grams. The same concept can be extended to ionic compounds and molecules. One formula unit of sodium chloride (NaCl) would weigh 58.44 amu (22.98977 amu for Na + 35.453 amu for Cl), so a mole of sodium chloride would weigh 58.44 grams. One molecule of water (H2O) would weigh 18.02 amu (2×1.00797 amu for H + 15.9994 amu for O), and a mole of water molecules would weigh 18.02 grams.
Atomic Element Mn
Periodic Table Element Names
The original periodic table of the elements published by Dimitri Mendeleev in 1869 arranged the elements that were known at the time in order of increasing atomic weight, since this was prior to the discovery of the nucleus and the interior structure of the atom. The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number instead.
